08. Sigmoid 函数
以下是上一道练习我的解决方案:
class Linear(Node):
def __init__(self, X, W, b):
# Notice the ordering of the inputs passed to the
# Node constructor.
Node.__init__(self, [X, W, b])
def forward(self):
X = self.inbound_nodes[0].value
W = self.inbound_nodes[1].value
b = self.inbound_nodes[2].value
self.value = np.dot(X, W) + b我的解决方案没有什么特别之处。我从相应的输入中获取了 X、W 和 b 的值。我使用了 np.dot 来处理矩阵乘法。
神经网络利用替代转换和激活函数更好地归类输出。S 型函数是最常用的激活函数之一。
Sigmoid 函数
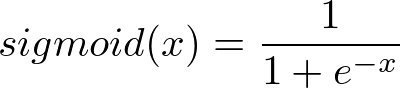
等式 (3)
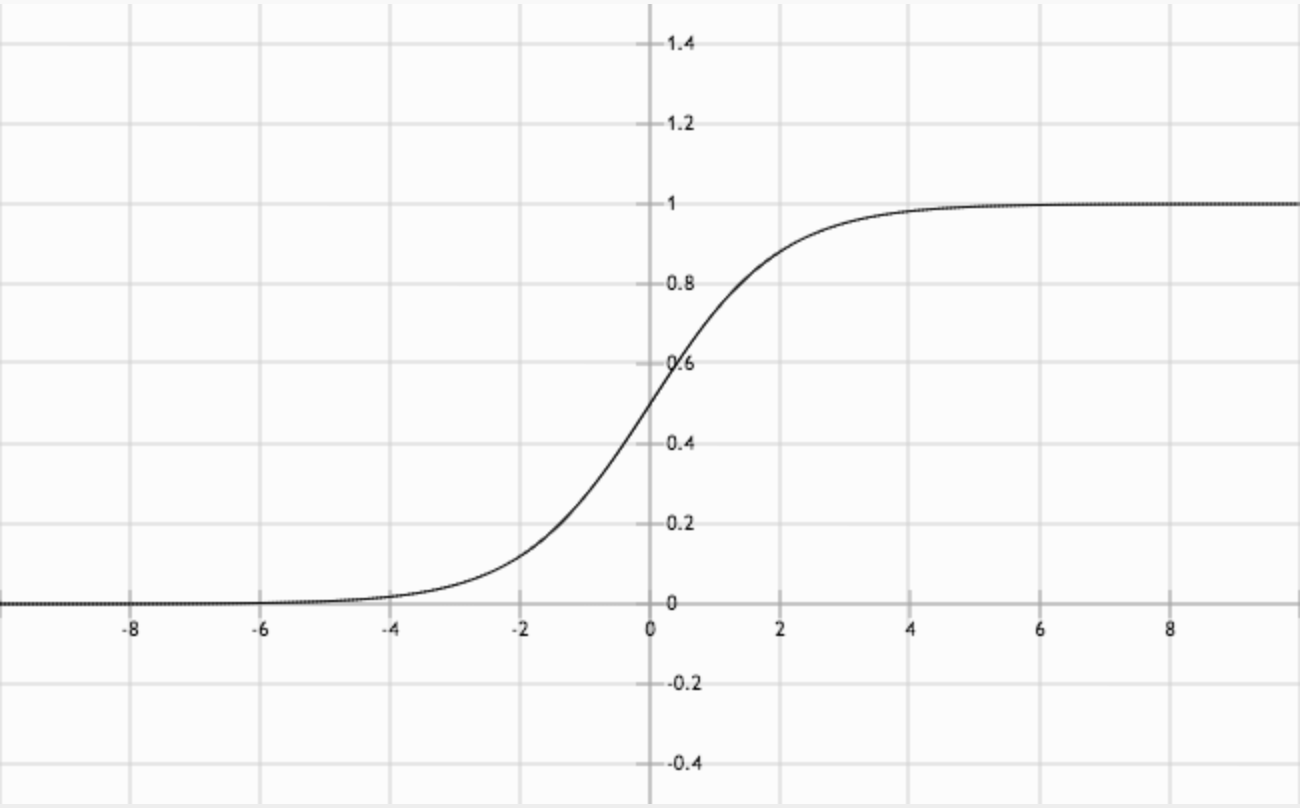
S 型函数图表。注意“S”型形状。
线性变换可以进行简单的值变换,但是神经网络通常需要更细致的变换。例如,人工神经元的原始设计之一——感知机就会出现二级制输出行为。感知机将加权输入与阈值对比。当加权输入超过该阈值,感知机就会被激活并输出 1,否则输出 0。
你可以用阶梯函数表示感知机的行为。
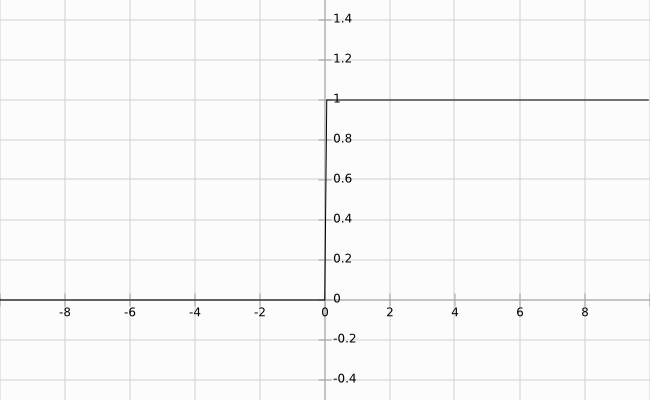
阶梯函数示例 (y = 0 和 y = 1 之间的跳转应该瞬间发生)。
激活(二进制输出行为这一概念)通常可以解决分类问题。例如,如果你要神经网络推测某个手写图片是否为 ‘9’,就相当于寻求二进制输出——是,是 ’9’,或者否,不是 ‘9’。阶梯函数是最纯粹的二进制输出形式,这很棒。但是,阶梯函数不是连续的,不可微,这很糟糕。可微分的函数才能产生梯度下降。
S 型函数(上述等式 (3))将阈值替换成美观的 S 型曲线(如上所示),模仿出感知机的激活行为,并且保持连续性,因此可微分。此外,S 型函数具有非常简单的导数,和 S 型曲线本身非常相似。
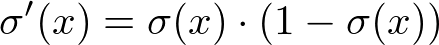
等式 (4). σ 表示等式 (3)
注意 S 型函数只有一个参数。注意,S 型函数是激活 函数(非线性),意味着它传入一个输入,并对其进行数学运算。
从概念上讲,S 型函数会做出决策。它会根据数据中的加权特征判断特征对某个分类产生影响。这样,S 型激活在线性变换后可以很好地运转。它现在具有随机权重和偏置,S 型节点的输出也是随机的。通过反向传播和梯度下降进行学习的流程(你很快就要实现这一点)会修改权重和偏置,使 S 型节点的激活开始于预期输出匹配。
注意,我已经提供了 S 型函数的等式。请将该等式添加到 MiniFlow 库中。为此,你需要使用 np.exp (documentation),这样操作起来更轻松。
你将使用 Sigmoid 和 Linear,如下所示:
输入 > 线性变换 > S 型函数
说明
- 打开 nn.py,看看网络是如何使用的
Sigmoid。 - 打开 miniflow.py。修改
Sigmoid类的forward方法,以反映 S 型函数的行为。 - 测试你的代码!当
Sigmoid能正常运转时,点击“提交”。
Start Quiz: