06. 学习和损失
学习和损失
就像当前状态的 MiniFlow 一样,神经网络传入输入并产生输出。但是与当前状态的 MiniFlow 不一样,神经网络可以逐渐改善其输出的准确性(很难想象 Add 会逐渐提高准确性!)。要理解为何准确性很重要,请首先实现一个比 Add 更难(也更实用)的节点。
线性方程
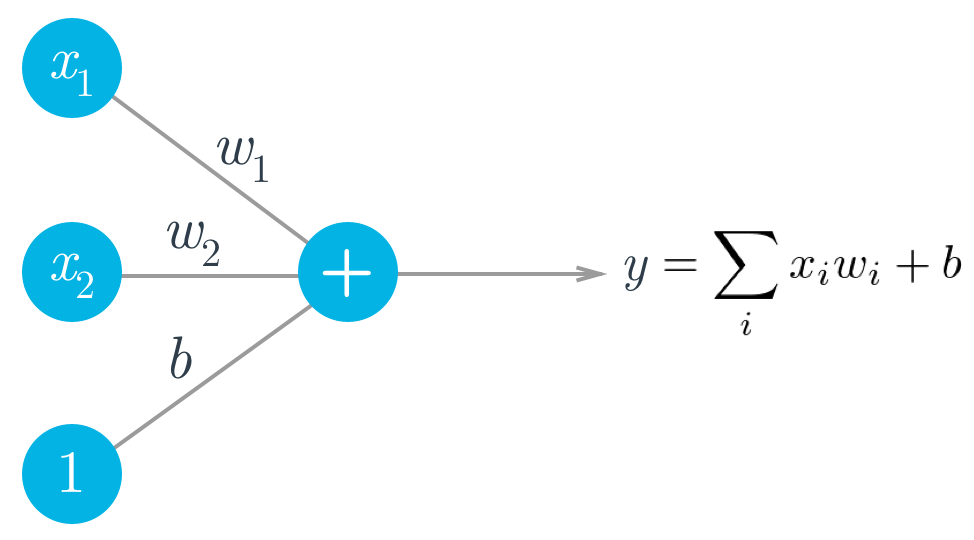
回忆下神经网络入门那部分课程。简单的人工神经元取决于以下三个组件:
- 输入, x_i
- 权重, w_i
- 偏置, b
输出 y 就是输入加上偏置的加权和。
注意,通过更改权重,你可以更改任何给定输入对输出带来的影响。神经网络的学习流程发生在反向传播过程中。在反向传播中,网络会修改权重,以改善网络的输出准确性。你很快将应用所有这些知识。
在下个测验中,你将构建一个线性神经元,该神经元通过应用简化的加权和生成输出。Linear 应该传入长为 n 的传入节点列表、长度为 n 的权重列表和偏置。
说明
- 打开下面的 nn.py。通读该神经网络,看看
Linear的预期输出结果。 - 打开下面的 miniflow.py。修改
Linear(Node的子类)以生成一个输出: y = \sum w_i x_i + b。
(提示,你可以使用 numpy 解答这道测验,但是也可以直接通过 Python 解答。)
Start Quiz: