18. 练习:TensorFlow Dropout
TensorFlow Dropout
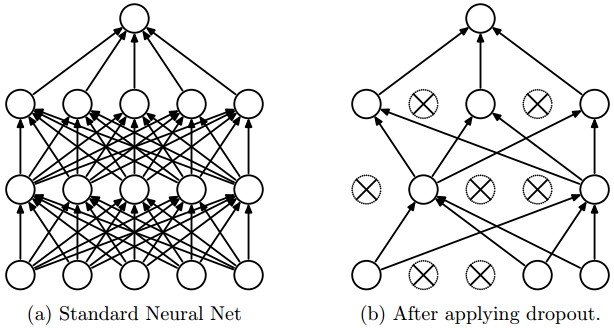
图 1:来自论文 "Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from
Overfitting" (https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/absps/JMLRdropout.pdf)
Dropout 是一个降低过拟合的正则化技术。它在网络中暂时的丢弃一些单元(神经元),以及与它们的前后相连的所有节点。图 1 是 dropout 的工作示意图。
TensorFlow 提供了一个 tf.nn.dropout() 函数,你可以用来实现 dropout。
让我们来看一个 tf.nn.dropout()的使用例子。
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # probability to keep units
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer, keep_prob)
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, weights[1]), biases[1])上面的代码展示了如何在神经网络中应用 dropout。
tf.nn.dropout()函数有两个参数:
hidden_layer:你要应用 dropout 的 tensorkeep_prob:任何一个给定单元的留存率(没有被丢弃的单元)
keep_prob 可以让你调整丢弃单元的数量。为了补偿被丢弃的单元,tf.nn.dropout() 把所有保留下来的单元(没有被丢弃的单元)* 1/keep_prob
在训练时,一个好的keep_prob初始值是0.5。
在测试时,把 keep_prob 值设为1.0 ,这样保留所有的单元,最大化模型的能力。
练习1
下面的代码,哪里出问题了?
语法没问题,但是测试准确率很低。
...
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # probability to keep units
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer, keep_prob)
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, weights[1]), biases[1])
...
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch_i in range(epochs):
for batch_i in range(batches):
....
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={
features: batch_features,
labels: batch_labels,
keep_prob: 0.5})
validation_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
features: test_features,
labels: test_labels,
keep_prob: 0.5})SOLUTION:
keep_prob 在评估验证准确率时应该设成 1.0练习 2
这个练习的代码来自 ReLU 的练习,应用一个 dropout 层。用 ReLU 层和 dropout 层构建一个模型,keep_prob值设为 0.5。打印这个模型的 logits。
注意: 由于 dropout 会随机丢弃单元,每次运行代码输出会有所不同。
Start Quiz: