14. 练习:TensorFlow ReLUs
TensorFlow ReLUs
TensorFlow 提供了 ReLU 函数 tf.nn.relu(),如下所示:
# Hidden Layer with ReLU activation function
# 隐藏层用 ReLU 作为激活函数
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, hidden_weights), hidden_biases)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
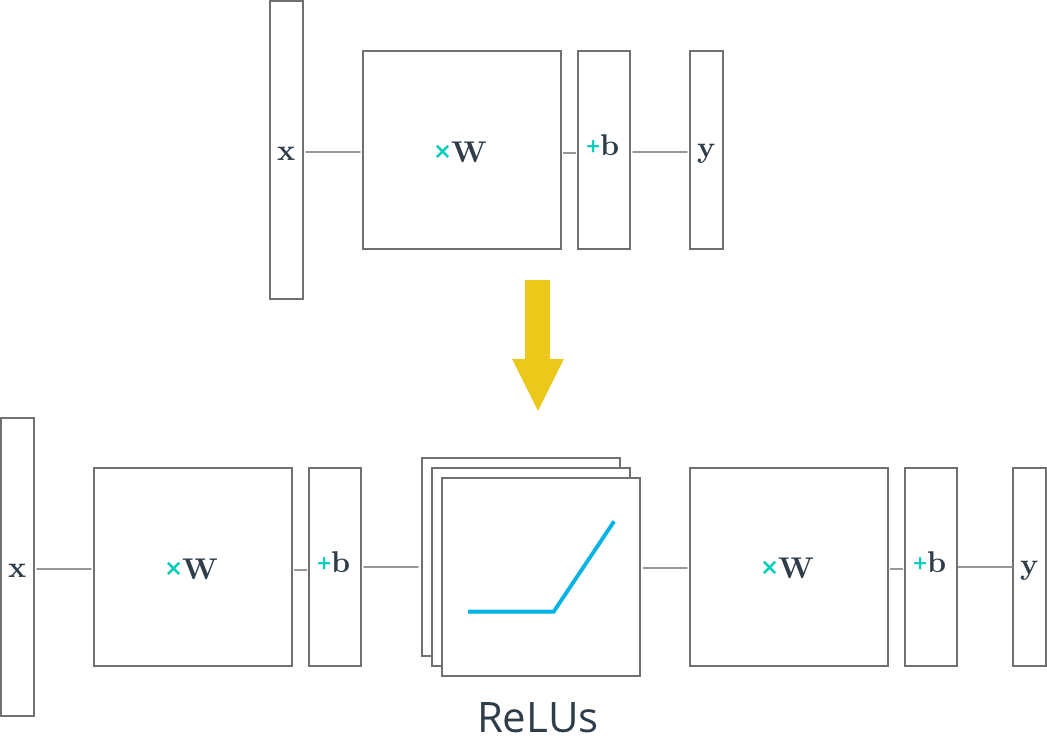
output = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, output_weights), output_biases)上面的代码把tf.nn.relu() 放到隐藏层,就像开关一样把负权重关掉了。在激活函数之后,添加像输出层这样额外的层,就把模型变成了非线性函数。这个非线性的特征使得网络可以解决更复杂的问题。
练习
下面你将用 ReLU 函数把一个线性单层网络转变成非线性多层网络。
Start Quiz: